Reference¶
Core¶
Core of BMS. All content of this file is imported by bms, and is therefore in bms
This file defines the base of BMS.
-
class
bms.core.Block(inputs, outputs, max_input_order, max_output_order)[source]¶ Bases:
objectAbstract class of block: this class should not be instanciate directly
-
class
bms.core.DynamicSystem(te, ns, blocks=[])[source]¶ Bases:
objectDefines a dynamic system that can simulate itself
Parameters: - te – time of simulation’s end
- ns – number of steps
- blocks – (optional) list of blocks defining the model
-
Save(name_file)[source]¶ name_file: name of the file without extension. The extension .bms is added by function
-
VariablesValues(variables, t)[source]¶ Returns the value of given variables at time t. Linear interpolation is performed between two time steps.
Parameters: - variables – one variable or a list of variables
- t – time of evaluation
-
graph¶
-
exception
bms.core.ModelError(message)[source]¶ Bases:
Exception-
args¶
-
with_traceback()¶ Exception.with_traceback(tb) – set self.__traceback__ to tb and return self.
-
-
class
bms.core.PhysicalBlock(physical_nodes, nodes_with_fluxes, occurence_matrix, commands, name)[source]¶ Bases:
objectAbstract class to inherit when coding a physical block
-
class
bms.core.PhysicalNode(cl_solves_potential, cl_solves_fluxes, node_name, potential_variable_name, flux_variable_name)[source]¶ Bases:
objectAbstract class
-
class
bms.core.PhysicalSystem(te, ns, physical_blocks, command_blocks)[source]¶ Bases:
objectDefines a physical system
-
dynamic_system¶
-
-
class
bms.core.Signal(names)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.VariableAbstract class of signal
-
values¶
-
-
class
bms.core.Variable(names='variable', initial_values=[0], hidden=False)[source]¶ Bases:
objectDefines a variable
Parameters: names – Defines full name and short name. If names is a string the two names will be identical otherwise names should be a tuple of strings (full_name,short_name)
Parameters: hidden – inner variable to hide in plots if true -
values¶
-
Signals¶
Functions¶
Collection of mathematical function signals
-
class
bms.signals.functions.Ramp(name='Ramp', amplitude=1, delay=0, offset=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.SignalCreate a Ramp with a certain amplitude, time delay and offset.
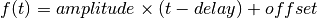
Parameters: - name (str) – The name of this signal.
- amplitude – The angular coefficient of the Ramp function.
- delay – The horizontal offset of the function.
- offset – The vertical offset of the function.
-
values¶
-
class
bms.signals.functions.SignalFunction(name, function)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.SignalCreate a signal based on a function defined by the user.
Parameters: - name (str) – The name of this signal.
- function – A function that depends on time.
-
values¶
-
class
bms.signals.functions.Sinus(name='Sinus', amplitude=1, w=1, phase=0, offset=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.SignalCreate a Sine wave with a certain amplitude, angular velocity, phase and offset.
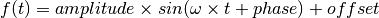
Parameters: - name (str) – The name of this signal.
- amplitude – The amplitude of the sine wave.
- w – The angular velocity of the sine wave (
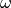 ).
). - phase – The phase of the sine wave.
- offset – The vertical offset of the function.
-
values¶
-
class
bms.signals.functions.Step(name='Step', amplitude=1, delay=0, offset=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.SignalCreate a Step with a certain amplitude, time delay and offset.
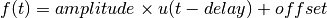
where
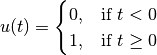
Parameters: - name (str) – The name of this signal.
- amplitude – The height of the step function.
- delay – The time to wait before the function stops being zero.
- offset – The vertical offset of the function.
-
values¶
WLTP signals¶
WLTP signals
-
class
bms.signals.wltp.WLTP1(name)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.SignalWLTP classe 1 cycle Caution! speed in m/s, not in km/h!
-
values¶
-
-
class
bms.signals.wltp.WLTP2(name)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.SignalWLTP classe 2 cycle Caution! speed in m/s, not in km/h!
-
values¶
-
-
class
bms.signals.wltp.WLTP3(name)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.SignalWLTP classe 3 cycle Caution! speed in m/s, not in km/h!
-
values¶
-
Blocks¶
Continuous Blocks¶
Collection of continuous blocks
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.DifferentiationBlock(input_variable, output_variable)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.blocks.continuous.ODECreates an ODE block that performs differentation of the input relative to time.
![output = \frac{d[input]}{dt}](_images/math/a51b4b0dc57918fc434f2b40186d4581cdd60324.png)
Parameters: - input_variable – This is the input or list of inputs of the block.
- output_variable (Variable) – This is the output of the block.
-
Evaluate(it, ts)¶
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
LabelConnections()¶
-
OutputMatrices(delta_t)¶
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.Division(input_variable1, input_variable2, output_variable)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines a division between its inputs.
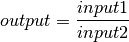
Parameters: -
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.FunctionBlock(input_variable, output_variable, function)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockThis defines a custom function over the input(s).
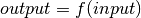
Parameters: - input_variable – This is the input or list of inputs of the block.
- output_variable (Variable) – This is the output of the block.
- function – This is the function that takes the inputs and returns the output.
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.Gain(input_variable, output_variable, value, offset=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines a gain operation.
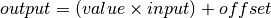
Parameters: -
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.IntegrationBlock(input_variable, output_variable)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.blocks.continuous.ODECreates an ODE block that performs integration of the input over time.
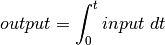
Parameters: - input_variable – This is the input or list of inputs of the block.
- output_variable (Variable) – This is the output of the block.
-
Evaluate(it, ts)¶
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
LabelConnections()¶
-
OutputMatrices(delta_t)¶
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.ODE(input_variable, output_variable, a, b)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines an ordinary differential equation based on the input.
a, b are vectors of coefficients so that H, the transfer function of the block, can be written as:
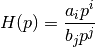
with Einstein sum on i and j, and p is Laplace’s variable.
For example,
a=[1], b=[0,1]is an integration, anda=[0,1], b=[1]is a differentiation.Parameters: -
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.Product(input_variable1, input_variable2, output_variable)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines a multiplication between its inputs.
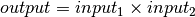
Parameters: -
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.Subtraction(input_variable1, input_variable2, output_variable)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines a subtraction between its two inputs.
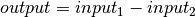
Parameters: -
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.Sum(inputs, output_variable)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines a sum over its inputs.
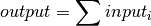
Parameters: - input_variable (list[Variables]) – This is the list of inputs of the block.
- output_variable (Variable) – This is the output of the block.
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
class
bms.blocks.continuous.WeightedSum(inputs, output_variable, weights, offset=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines a weighted sum over its inputs.
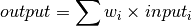
Parameters: - input_variable (list[Variables]) – This is the list of inputs of the block.
- output_variable (Variable) – This is the output of the block.
- weights – These are the weights that are multiplied by the elements of the input.
- offset – This offset is added to the final result.
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
Non-linear Blocks¶
Collection of non-linear blocks
-
class
bms.blocks.nonlinear.Coulomb(input_variable, speed_variable, output_variable, max_value, tolerance=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockReturn coulomb force under condition of speed and sum of forces (input)
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.nonlinear.CoulombVariableValue(external_force, speed_variable, value_variable, output_variable, tolerance=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockReturn coulomb force under condition of speed and sum of forces (input) The max value is driven by an input
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.nonlinear.Delay(input_variable, output_variable, delay)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockSimple block to delay output with respect to input.
Parameters: delay – a delay in seconds -
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.nonlinear.RegCoulombVariableValue(external_force, speed_variable, value_variable, output_variable, tolerance=0)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockReturn coulomb force under condition of speed and sum of forces (input) The max value is driven by an input
-
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-
-
class
bms.blocks.nonlinear.Saturation(input_variable, output_variable, min_value, max_value)[source]¶ Bases:
bms.core.BlockDefines a saturation block.
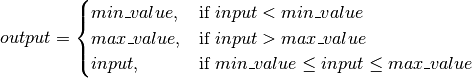
Parameters: -
InputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶ Returns the input values at a given iteration for solving the block outputs
-
OutputValues(it, nsteps=None)¶
-
Solve(it, ts)¶
-